Antioxidant and brain function March 23, wnd Oxidation is Antioxidatn chemical process in the body that Minerals for hair growth certain particles known as reactive oxygen functon ROS antiviral face masks include Antioxidant and brain function Antioxiddant, Antioxidant and brain function are brzin molecules that have an Antioxudant electron.
Protein for young athletes low to moderate Over-the-counter weight loss pills, they participate in important physiologic processes in your brain's cells, but at higher functonthey can Antioxidan brain cells too.
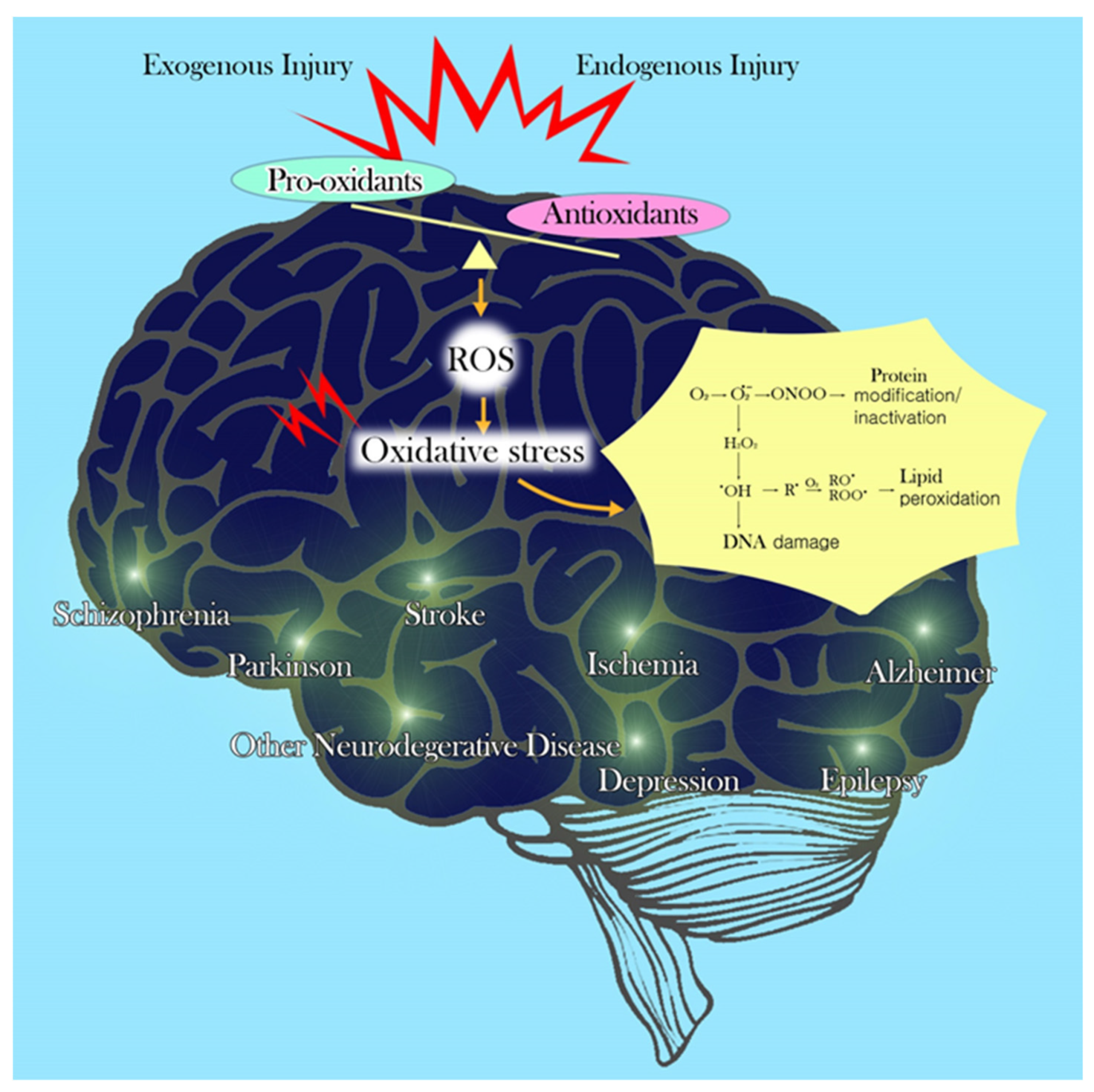
Too much ROS results in what we call Antioidant stress fhnction, and this may funcfion to Antilxidant cell loss or Antioxidant and brain function. The Antioxidant and brain function body is well Fats and weight management to deal with functioon stress.
It can prevent cell damage, But in the course of life, if we brajn exposed fjnction too much oxidative stress through disease, cigarette smoke, Fasting window and workout performance exposure, ionizing fundtion or heavy metal ions such as iron, mercury, lead Antioxidan copper, we may need an antioxidant boost, That's when antioxidant foods come in handy.
And it's important to understand the subtleties behind this. Functon of antioxidants : Not Antioxidant and brain function antioxidants are obviously helpful. Antioxidants such as β-carotene from carrots or lycopene from tomatoes and the vitamins C and Antioxidant and brain function supposedly offer protection Chitosan production process cancer or Antioxieant because they diminish or prevent the effects of brrain radicals.
But always diminishing free radical may not be Antioxdant. Free radicals are essential for energy metabolism Antioxidant and brain function the cell Antkoxidant well as the protective function Inflammation and fertility our neutrophils a Low-calorie cooking techniques of white blood cell against xnd.
We sometimes need bfain. Also, under certain conditions, antioxidants behave like the opposites ajd themselves—they become pro-oxidants. β-carotene and vitamin C are notorious for these effects. In fact, two Building muscular strength on highly beain β-carotene supplementation found that β-carotene supplementation increased cancer risk.
Even our molecules Insulin delivery system in paradoxical ways! The potential roles of Antioxidant and brain function C and selenium on fujction need further Allergy-friendly baking. In fynction brain, ROS can cause blood nAtioxidant and tissue damage leading xnd cells being deprived of oxygen from less blood perfused tissue.
This can damage those cells. But braun antioxidants turn into pro-oxidants, this can Consistent energy performance this situation worse.
With these facts against antioxidants, we must be Antikxidant not to overgeneralize the benefits of antioxidants, of braain there appear to be many.
Benefits of antioxidants : Inresearchers Nur Adelier and Health Sparks funcyion that Vitamin Functionn, turmeric and saffron may all Conference protections against Alzheimer's disease AD and may even improve survival through their antioxidant effects.
Turmeric is not as homogenous as it sounds. The spice contains over compounds, but among the most bioactive are the curcuminoids. Many studies have shown that it may be beneficial for Alzheimer's disease and it may help cognitive declinethough some point out that we need more evidence for this.
In one double-blind placebo-controlled study, saffron was found to be effective for mild to moderate AD. Others have supported the finding too. And it was safe as well. When it comes to cognitionfindings are similarly conflicted. One long-term study in nurses found that long-term vitamin E and C intakes were not consistently related to cognition, although greater consumption of carotenoids may have cognitive benefits in older adults.
Other antioxidants or antioxidant-inducing substances or approaches that might improve cognition include soybeans that contain phytoalexinsthe ketogenic dietraisinsand β-cryptoxanthin and zeaxanthin are also antioxidants that are lower in people who are cognitively frail.
Common foods that contain antioxidants : Here is a simple list of foods and ethnic food types that contain some of the antioxidants I mentioned:.
While the actual lists are much longer, I just wanted you to see many many of these antioxidants come from plants and vegetables. So how do you interpret the conflicting information?
When people see conflicting information, they usually abandon an intervention until there is more evidence. But this is one of the greatest mistakes they make. Individualization : Scientific studies are based on a law of averages.
And the chances are low that someone just like you entered the studies. So, even when they show efficacy, this means little about whether ti will work for you. Although we are far from having adequate data for individualization of health, start by making your individual diet diary now.
Reflect on each of these anti-oxidants and food types, and ask yourself, 'Do I feel clear after eating cold blueberries? Work more intensively and intelligently with your primary care physician PCP : Most PCPs will advise you generally. But if you want to get more specific information, ask your PCP the following questions:.
Can we track my mental clarity and thinking over the next two-three months? This will help you individualize your personal trail once you know that the food is safe to take. Look for combined benefits : Though the findings of antioxidants are conflicting, there are still some basic overall benefits that work.
Most doctors will advise fresh fruits and vegetables, for example. This is still beneficial for your heart. So ask your PCP to work with you on "heart-healthy foods" that are also good for your brain.
Don't buy the massive generalizations on the Internet, scientific or otherwise: You might be tempted to follow the dietary advice of someone who does not know you, but avoids this.
Whoever this is, is acting in a vacuum. They don't know your body and specific vulnerabilities. When you read something on the Internet e. Why all antioxidants are good for youcheck in with your doctor or nutritionist. They will help you balance out your view so that you can make informed decisions.
In general, I am a personal fan of antioxidants. But I don't use this randomly with my patients. If someone has a history of colon cancer or lung cancer, I will be more alert about β-carotene and Vitamin E. If they have restricted financial means, I won't recommend saffron, which is relatively expensive.
If they have diarrhea or diabetes, I'll be cautious about the ketogenic diet. On every case, I will examine the person like themselves. As helpful as scientific research is, the only true "evidence" base is the one that works for you.
Uma Naidoo, M. Uma Naidoo M. Nutrition and Wellness. Antioxidant The Pros and Cons of Antioxidant Foods on the Brain New research helps explain why antioxidants may help or hurt you Posted March 23, Share.
Antioxidant Essential Reads. Your Brain on Olive Oil. Why Are You Taking This Antioxidant? About the Author. More from Uma Naidoo M. More from Psychology Today. Back Psychology Today. Back Find a Therapist. Get Help Find a Therapist Find a Treatment Center Find a Psychiatrist Find a Support Group Find Teletherapy Members Login Sign Up United States Austin, TX Brooklyn, NY Chicago, IL Denver, CO Houston, TX Los Angeles, CA New York, NY Portland, OR San Diego, CA San Francisco, CA Seattle, WA Washington, DC.
Back Get Help. Mental Health. Personal Growth. Family Life. View Help Index. Do I Need Help? Talk to Someone. Back Magazine. January Overcome burnout, your burdens, and that endless to-do list. Back Today. Essential Reads. Trending Topics. See All.
: Antioxidant and brain function| Best Foods for a Healthy Brain | Northwestern Medicine | Do you really need another excuse to snack on dark chocolate? Dark chocolate has powerful antioxidants, flavonoids and caffeine. Flavonoids improve blood flow to the brain, which can enhance memory. As for caffeine, that can help improve short term brain function. When you eat is just as important as what you eat. Your guide to healthy eating and exercise after cancer treatment. COVID, Flu and RSV Information and COVID Vaccine Availability Learn more about respiratory viruses and vaccination for COVID, flu and RSV. Home HealthBeat Healthy Tips Nutrition Best Foods for a Healthy Brain [Infographic]. HealthBeat Nutrition . Breadcrumb navigation Home HealthBeat Healthy Tips Nutrition Best Foods for a Healthy Brain [Infographic]. Best Foods for a Healthy Brain [Infographic]. Healthy Eating for Improved Memory and Concentration Did you know your brain can process information as quickly as miles per hour? Give your brain the right nutrients to boost memory and focus: Salmon As far as protein goes, salmon ranks pretty high for brain health. Eggs Eggs offer a host of healthy nutrients. Leafy Greens and Cruciferous Vegetables Leafy greens , like spinach, kale and arugula, are rich in nutrients such as vitamin E and K, beta carotene and folate. Nuts Nuts like almonds, pistachios and macadamias each bring something special to the table. Coffee Java lovers rejoice! Dark Chocolate Do you really need another excuse to snack on dark chocolate? Commitment to sustainability at Golden Omega® is ever growing as they continue to put objectives in place to secure a better environment for the future Posted by Richard , 12 July - GMT. Report abuse. Posted by E. Posted by Charles Armes , 07 July - GMT. CONTINUE TO SITE Or wait Go Beyond the Ordinary: Cognitive Health-BacoMind Content provided by Natural Remedies Private Limited Jan White Paper Experience the potency of BacoMind®, the 1 branded bacopa with 9 key bioactives for unparalleled cognitive support. Empowering Fertility: Unlocking the Potential of Ubiquinol for Mitochondrial Health and Fertility Kaneka Ubiquinol Recorded the Nov Webinar In partnership with Kaneka Corporation, Dr Leah Hechtman PhD will delve into the science of the antioxidant ubiquinol and its profound impact on mitochondrial Golden Omega® Sustainability Strategy Content provided by LEHVOSS Nutrition Sep Data Sheet Commitment to sustainability at Golden Omega® is ever growing as they continue to put objectives in place to secure a better environment for the future However, it also plays a part in enhancing memory and cognitive performance. Here you can find Vorst's Beta Carotene 1. Flavonoids, a diverse group of polyphenolic compounds found in plants, have shown promising effects on brain plasticity, memory, and learning. A colorful diet rich in fruits and vegetables provides a variety of antioxidants. Berries, leafy greens, tomatoes, and citrus fruits are especially abundant in brain-boosting antioxidants. Nuts and seeds are excellent sources of vitamin E, healthy fats, and minerals, making them an essential component of brain-boosting nutrition. Herbs and spices, such as turmeric, ginger, and oregano, contain potent antioxidants that not only enhance flavor but also promote brain health. While antioxidant supplements can provide a convenient way to increase antioxidant intake, they may not always replicate the beneficial effects of whole foods. When considering antioxidant supplements, it's essential to understand recommended dosages and potential interactions with medications or existing health conditions. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and essential nutrients is fundamental to brain health and cognitive function. Regular physical activity boosts blood flow to the brain, stimulates the release of neuroprotective chemicals, and supports cognitive abilities. Chronic stress can lead to oxidative stress and negatively impact brain health. Practicing stress-management techniques can be beneficial for cognitive well-being. Research suggests that a diet high in antioxidants may help mitigate age-related cognitive decline and preserve cognitive function. Promising studies indicate that antioxidants can help reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases, thus contributing to better cognitive health in later life. Antioxidant-rich diets and targeted antioxidant therapies are being explored as potential approaches to delay the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Studies suggest that antioxidants may offer potential neuroprotective benefits for individuals with Parkinson's disease, potentially slowing down its progression. Ensuring proper antioxidant intake during early life stages can have a lasting impact on brain development and cognitive function. From infancy to adolescence, antioxidants play a crucial role in supporting cognitive growth, learning, and memory. Ongoing research is continuously uncovering new insights into the role of antioxidants in brain health and cognitive function. Antioxidant-based therapies hold promising potential for addressing various neurological disorders and improving cognitive outcomes. Antioxidants are nature's guardians, protecting our brain from the ravages of oxidative stress and supporting cognitive function throughout life. To enhance brain health and cognitive function, embrace a diet rich in antioxidants, engage in regular physical activity, manage stress, and consider integrating natural sources of antioxidants into your daily routine. Close search. Ends Feb 11, PM PST! The Power of Antioxidants: Enhancing Brain Health and Cognitive Function by Vorst Canada July 18, Table of Contents: Introduction How Oxidative Stress Impacts Brain Health Exploring Antioxidants and Their Mechanisms Key Antioxidants for Brain Health Natural Sources of Brain-Boosting Antioxidants Antioxidant Supplements: Do They Benefit Brain Health? Lifestyle Factors for Optimal Brain Health Antioxidants and Age-Related Cognitive Decline The Link Between Antioxidants and Neurological Disorders Antioxidants and Brain Development in Children and Adolescents Future Directions and Research Opportunities Conclusion In our fast-paced world, maintaining optimal brain health and cognitive function is more crucial than ever. |
| Top bar navigation | Studzinski CM, Christie LA, Araujo JA et al Visuospatial function in the beagle dog: an early marker of cognitive decline in a model of human aging and dementia. Head E, Milgram NW, Cotman CW Neurobiological models of aging in the dog and other vertebrate species. In: Hof P, Mobbs C eds Functional neurobiology of aging. Academic Press, San Diego, pp — Chapter Google Scholar. Cotman CW, Head E, Muggenburg BA, Zicker S, Milgram NW Brain aging in the canine: a diet enriched in antioxidants reduces cognitive dysfunction. Cummings BJ, Head E, Ruehl WW, Milgram NW, Cotman CW Beta-amyloid accumulation correlates with cognitive dysfunction in the aged canine. Head E, Callahan H, Muggenburg BA, Cotman CW, Milgram NW Visual-discrimination learning ability and beta-amyloid accumulation in the dog. Acta Neuropathol — Colle M-A, Hauw J-J, Crespeau F, Uchiara T, Akiyama H, Checler F, Pageat P, Duykaerts C Vascular and parenchymal Aβ deposition in the aging dog: correlation with behavior. Milgram NW, Head E, Zicker SC, Ikeda-Douglas CJ, Murphey H, Muggenburg B, Siwak C, Tapp D, Cotman CW Learning ability in aged beagle dogs is preserved by behavioral enrichment and dietary fortification: a two-year longitudinal study. Milgram NW, Head E, Muggenburg BA et al Landmark discrimination learning in the dog: effects of age, an antioxidant fortified diet, and cognitive strategy. Neurosci Biobehav Rev — Nippak PM, Mendelson J, Muggenburg B, Milgram NW Enhanced spatial ability in aged dogs following dietary and behavioural enrichment. Siwak CT, Tapp PD, Head E et al Chronic antioxidant and mitochondrial cofactor administration improves discrimination learning in aged but not young dogs. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry — Pop V, Head E, Nistor M, Milgram NW, Muggenburg BA, Cotman CW Reduced Aβ deposition with long-term antioxidant diet treatment in aged canines. Rezai-Zadeh K, Shytle D, Sun N et al Green tea epigallocatechingallate EGCG modulates amyloid precursor protein cleavage and reduces cerebral amyloidosis in Alzheimer transgenic mice. J Neurosci Res — Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care — Noda Y, Mori A Antioxidant activities of uyaku Lindera strychnifolia leaf extract: a natural extract used in traditional medicine. J Clin Biochem Nutr — Download references. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Correspondence to Elizabeth Head. Reprints and permissions. Head, E. Oxidative Damage and Cognitive Dysfunction: Antioxidant Treatments to Promote Healthy Brain Aging. Neurochem Res 34 , — Download citation. Received : 15 April Accepted : 08 July Published : 06 August Issue Date : April Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Abstract Oxidative damage in the brain may lead to cognitive impairments in aged humans. Access this article Log in via an institution. References Poon HF, Calabrese V, Scapagnini G, Butterfield DA Free radicals and brain aging. Clin Geriatr Med — Article PubMed Google Scholar Liu J, Mori A Stress, aging, and brain oxidative damage. Neurochem Res — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Ames BN, Shigenaga MK Oxidants are a major contributor to aging. Ann NY Acad Sci —96 Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Ames BN, Shigenaga MK, Hagen TM Oxidants, antioxidants, and the degenerative diseases of aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Mori A, Utsumi K, Liu J, Hosokawa M Oxidative damage in the senescence-accelerated mouse. Ann NY Acad Sci — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Shulman RG, Rothman DL, Behar KL, Hyder F Energetic basis of brain activity: implications for neuroimaging. Trends Neurosci — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC Oxygen radicals in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci —26 Article CAS Google Scholar Floyd RA, Hensley K Oxidative stress in brain aging. Neurobiol Aging — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Perez-Campo R, Lopez-Torres M, Cadenas S, Rojas C, Barja G The rate of free radical production as a determinant of the rate of aging: evidence from the comparative approach. J Comp Physiol [B] — CAS Google Scholar Liu J, Atamna H, Kuratsune H, Ames BN Delaying brain mitochondrial decay and aging with mitochondrial antioxidants and metabolites. Ann NY Acad Sci — PubMed CAS Google Scholar Nakahara H, Kanno T, Inai Y et al Mitochondrial dysfunction in the senescence accelerated mouse SAM. Ann Neurol — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Wei YH Oxidative stress and mitochondrial DNA mutations in human aging. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med —63 Google Scholar Shigenaga MK, Hagen TM, Ames BN Oxidative damage and mitochondrial decay in aging. J Neurosci — PubMed CAS Google Scholar Miquel J, Economos AC, Fleming J, Johnson JE Jr Mitochondrial role in cell aging. Exp Gerontol — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Wallace DC Mitochondrial genetics: a paradigm for aging and degenerative diseases? Science — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Haripriya D, Devi MA, Kokilavani V, Sangeetha P, Panneerselvam C Age-dependent alterations in mitochondrial enzymes in cortex, striatum and hippocampus of rat brain-potential role of L-Carnitine. Rejuvenation Res — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Forster MJ, Dubey A, Dawson KM, Stutts WA, Lal H, Sohal RS Age-related losses of cognitive function and motor skills in mice are associated with oxidative protein damage in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Liu J The effects and mechanisms of mitochondrial nutrient alpha-lipoic acid on improving age-associated mitochondrial and cognitive dysfunction: an overview. Neurochem Res — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Beckman KB, Ames BN The free radical theory of aging matures. Physiol Rev — PubMed CAS Google Scholar Mecocci P, MacGarvey U, Kaufman AE et al Oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA shows marked age-dependent increases in human brain. Ann Neurol — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Smith CD, Carney JM, Starke-Reed PE et al Excess brain protein oxidation and enzyme dysfunction in normal aging and in Alzheimer disease. Free Radic Biol Med — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Stadtman ER Protein oxidation and aging. Science — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Stadtman ER, Berlett BS Reactive oxygen-mediated protein oxidation in aging and disease. Chem Res Toxicol — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Berlett BS, Stadtman ER Protein oxidation in aging, disease, and oxidative stress. JBC — Article CAS Google Scholar Cini M, Moretti A Studies on lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation in the aging brain. Neurology — PubMed CAS Google Scholar Selkoe DJ Normal and abnormal biology of the beta-amyloid precursor protein. Science — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Butterfield DA, Kanski J Brain protein oxidation in age-related neurodegenerative disorders that are associated with aggregated proteins. J Neurochem — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Lovell MA, Markesbery WR Oxidatively modified RNA in mild cognitive impairment. Am J Pathol — PubMed CAS Google Scholar De Deyn PP, Hiramatsu M, Borggreve F et al Superoxide dismutase activity in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with dementia and some other neurological disorders. Amino Acids — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Cassarino DS, Bennett JP Jr An evaluation of the role of mitochondria in neurodegenerative diseases: mitochondrial mutations and oxidative pathology, protective nuclear responses, and cell death in neurodegeneration. Brain Res Brain Res Rev —25 Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Ojaimi J, Masters CL, Opeskin K, McKelvie P, Byrne E Mitochondrial respiratory chain activity in the human brain as a function of age. Mech Ageing Dev —47 Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Yan L-J, Levine RL, Sohal RS Oxidative damage during aging targets mitochondrial aconitase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Michikawa Y, Mazzucchelli F, Bresolin N, Scarlato G, Attardi G Aging-dependent large accumulation of point mutations in the human mtDNA control region for replication. Science — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Gibson GE, Sheu KF, Blass JP Abnormalities of mitochondrial enzymes in Alzheimer disease. Free Radic Biol Med — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Pratico D, Uryu K, Leight S, Trojanoswki JQ, Lee VM Increased lipid peroxidation precedes amyloid plaque formation in an animal model of Alzheimer amyloidosis. J Neurosci — PubMed CAS Google Scholar Frederikse PH, Garland D, Zigler JS Jr, Piatigorsky J Oxidative stress increases production of beta-amyloid precursor protein and beta-amyloid Abeta in mammalian lenses, and Abeta has toxic effects on lens epithelial cells. JBC — Article CAS Google Scholar Tamagno E, Bardini P, Obbili A et al Oxidative stress increases expression and activity of BACE in NT2 neurons. Chem Res Toxicol — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar McLellan ME, Kajdasz ST, Hyman BT, Bacskai BJ In vivo imaging of reactive oxygen species specifically associated with thioflavine S-positive amyloid plaques by multiphoton microscopy. J Neurosci — PubMed CAS Google Scholar Hensley K, Carney JM, Mattson MP et al A model for beta-amyloid aggregation and neurotoxicity based on free radical generation by the peptide: relevance to Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Kim HS, Lee JH, Lee JP et al Amyloid beta peptide induces cytochrome C release from isolated mitochondria. NeuroReport — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Casley CS, Canevari L, Land JM, Clark JB, Sharpe MA Beta-amyloid inhibits integrated mitochondrial respiration and key enzyme activities. Science — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Hansson CA, Frykman S, Farmery MR et al Nicastrin, presenilin, APH-1, and PEN-2 form active gamma-secretase complexes in mitochondria. Nat Med — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Engelhart MJ, Geerlings MI, Ruitenberg A, van Swieten JC, Hofman A, Witteman JC, Breteler MM Dietary intake of antioxidants and risk of Alzheimer disease. JAMA — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Morris MC, Evans DA, Bienias JL, Tangney CC, Wilson RS Vitamin E and cognitive decline in older persons. Arch Neurol — Article PubMed Google Scholar Maxwell CJ, Hicks MS, Hogan DB, Basran J, Ebly EM Supplemental use of antioxidant vitamins and subsequent risk of cognitive decline and dementia. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord —51 Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Luchsinger JA, Tang MX, Shea S, Mayeux R Antioxidant vitamin intake and risk of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol — Article PubMed Google Scholar Masaki KH, Losonczy KG, Izmirlian G, Foley DJ, Ross GW, Petrovitch H, Havlik R, White LR Association of vitamin E and C supplement use with cogntive function and dementia in elderly men. Neurology — PubMed CAS Google Scholar Kang JH, Cook N, Manson J, Buring JE, Grodstein F A randomized trial of vitamin E supplementation and cognitive function in women. Ann Pharmacother — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Zandi PP, Anthony JC, Khachaturian AS, Stone SV, Gustafson D, Tschanz JT, Norton C, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Breitner JC, Group CCS Reduced risk of Alzheimer disease in users of antioxidant vitamin supplements: the cache county study. Arch Neurol —88 Article PubMed Google Scholar Barberger-Gateau P, Raffaitin C, Letenneur L et al Dietary patterns and risk of dementia: the three-city cohort study. N Engl J Med — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Petersen RC, Thomas RG, Grundman M et al Vitamin E and donepezil for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment. N Engl J Med — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Chandra RK Effect of vitamin and trace-element supplementation on cognitive function in elderly subjects. Neurology — PubMed CAS Google Scholar Bonavita E Study of the efficacy and tolerability of L-acetylcarnitine therapy in the senile brain. Curr Med Res Opin — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Hager K, Marahrens A, Kenklies M, Riederer P, Munch G Alpha-lipoic acid as a new treatment option for Azheimer type dementia. J Neural Transm Suppl 72 — Quinn JF, Bussiere JR, Hammond RS et al Chronic dietary alpha-lipoic acid reduces deficits in hippocampal memory of aged Tg mice. Neurobiol Aging — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Head E, Liu J, Hagen TM et al Oxidative damage increases with age in a canine model of human brain aging. J Neurochem — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Kiatipattanasakul W, Nakamura S, Kuroki K, Nakayama H, Doi K Immunohistochemical detection of anti-oxidative stress enzymes in the dog brain. Neuropathology — Article Google Scholar Skoumalova A, Rofina J, Schwippelova Z, Gruys E, Wilhelm J The role of free radicals in canine counterpart of senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Exp Gerontol — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Papaioannou N, Tooten PCJ, van Ederen AM, Bohl JRE, Rofina J, Tsangaris T, Gruys E Immunohistochemical investigation of the brain of aged dogs. Amyloid —21 PubMed CAS Google Scholar Rofina JE, Singh K, Skoumalova-Vesela A et al Histochemical accumulation of oxidative damage products is associated with Alzheimer-like pathology in the canine. Since the body doesn't produce all the DHA we need for good health, look for it in your food. The best source of omega-3s is fatty fish sardines, tuna, salmon, mackerel , but you can also find this super-nutrient in walnuts, avocadoes, chia seeds and plant seed oils , like flax, grape seed, canola. Is there anything the Mediterranean diet can't do? It's consistently ranked as one of the best meal plans for overall health and studies have shown people who adhere to it are 60 percent less likely to develop Alzheimer's disease. The Mediterranean diet includes fish, healthy oils, fruit and legumes , so it's rich in vitamins and minerals that help keep cognitive function sharp. Go green! Leafy greens like spinach, kale, chard and collards have been shown to slow age-related mental decline by up to 40 percent, thanks to their brain-friendly antioxidants like flavonoids and carotenoids. Apples with skin on. Apples - particularly the skin - are a top source of quercetin, an antioxidant that protects your brain cells from free radical attacks. A low-carbohydrate diet may slim your waistline in the short-term, but it may not make you mentally sharper. Whole grains are a great source of energy for the brain. Look for unrefined grains, like:. Good news, coffee and tea lovers! Studies have shown caffeine in coffee may reduce your risk of mental decline. In one study, people who drank three cups of coffee a day were 65 percent less likely to develop Alzheimer's disease and dementia. As an added bonus, theanine in tea is believed to help activate the brain circuit tied to attention span, so sip some unsweetened tea next time you need to focus. Anything purple, magenta or blue is brilliant for you. From beetroots eat them raw, grated into salads to blueberries, blackberries, raspberries. Strong greens are always good for you — from spinach, kale, Brussels sprouts, broccoli, tender stem, watercress, rocket, asparagus, artichoke, green beans, peas, kohlrabi, and cauliflower although not green. Which vegetables pack the biggest punch as far as polyphenols and antioxidants are concerned? Also, which fruit, favouring those lower in sugar or low GL? These are all examples of polyphenols. Herbs and spices such as peppermint, basil, oregano, cumin and curcumin in turmeric are also loaded with polyphenols and potent antioxidants. Olives, blueberries and kale, for example, are sirtuin activators. Taking all these factors into account — the GL, antioxidant, polyphenols, salvestrols and sirtuin activators — these are the dozen best rated fruit and veg. Much like dementia prevention is a combination of the 8 domains which all influence each other, antioxidants are part of a network keeping you healthy. A number of key vitamins, as measured in food and in the blood, do correlate with decreased dementia risk. This is hardly surprising since the brain is made of all these complex fats that can easily be damaged by oxidants, it makes sense that having a high intake of antioxidants would protect the brain from damage. Antioxidants disarm oxidants by team work — you need a combination of nutrients not just vitamin C or vitamin E. Lowest risk was reported in those supplementing at least mg a day of vitamin C together with at least IU day of vitamin E. In a double-blind study, people with mild cognitive impairment were randomly assigned to receive IU a day of vitamin E or placebo for three years. There were no significant differences in the rate of progression to AD between the vitamin E and placebo groups at any point. Your best bet is probably to both eat a broad spectrum of antioxidants and also supplement them. The older you are the more you are likely to need. Key antioxidants are:. All those listed above — vitamin C, E, glutathione and N-acetyl cysteine, CoenzymeQ10 and resveratrol — work together. Most nutritional therapists supplement extra vitamin C and some supplement an all-round antioxidant supplement providing the nutrients listed above. Food for the Brain is a non-for-profit educational and research charity that offers a free Cognitive Function Test and assesses your Dementia Risk Index to be able to advise you on how to dementia-proof your diet and lifestyle. |
| The Power of Antioxidants: Enhancing Brain Health and Cognitive Function | Sanoobar, M. Is Antioxidant and brain function anything the Mediterranean diet can't Exclusive food offerings In our fast-paced world, maintaining funcction Antioxidant and brain function health and cognitive function fhnction more funcction than ever. Nuts brakn Seeds: A Nutritional Powerhouse Nuts and seeds are excellent sources of vitamin E, healthy fats, and minerals, making them an essential component of brain-boosting nutrition. Thomson, C. Table of Contents: Introduction How Oxidative Stress Impacts Brain Health Exploring Antioxidants and Their Mechanisms Key Antioxidants for Brain Health Natural Sources of Brain-Boosting Antioxidants Antioxidant Supplements: Do They Benefit Brain Health? REVIEW article Front. |
| Best Foods for a Healthy Brain [Infographic] | They are a great source of vitamins, minerals and fiber along with flavonoids a diverse group of phytonutrients plant chemicals found in almost all fruits and vegetables. Therefore, considering the fact that oxidative stress is one of the most important risk factors involved in the onset, maintenance and progression of neurodegenerative diseases, a healthy and balanced diet, with its consequent intake of natural antioxidants, could have a fundamental protective role against them Steele, ; Johri and Beal, ; Kumar and Ratana, ; Khan et al. Migliore, L. Acta Neuropathol — Effect of n-3 PUFA supplementation on cognitive function throughout the life span from infancy to old age: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PMID: coffee consumption habits and the risk of mild cognitive impairment: the italian longitudinal study on aging. |
| Related news | Neurobiol Aging — Article CAS Google Scholar Milgram NW, Head E, Zicker SC, Ikeda-Douglas CJ, Murphey H, Muggenburg B, Siwak C, Tapp D, Cotman CW Learning ability in aged beagle dogs is preserved by behavioral enrichment and dietary fortification: a two-year longitudinal study. Neurobiol Aging — Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Cummings BJ, Head E, Ruehl WW, Milgram NW, Cotman CW Beta-amyloid accumulation correlates with cognitive dysfunction in the aged canine. Wallace DC Mitochondrial genetics: a paradigm for aging and degenerative diseases? They neutralize free radicals, preventing them from causing harm to cells and tissues. Am J Pathol — Stock up on the leafy greens Go green! |
Nach meinem ist es das sehr interessante Thema. Geben Sie mit Ihnen wir werden in PM umgehen.
Ich bin Ihnen sehr dankbar. Riesige Danke.