Coenzyme Q for heart disease -
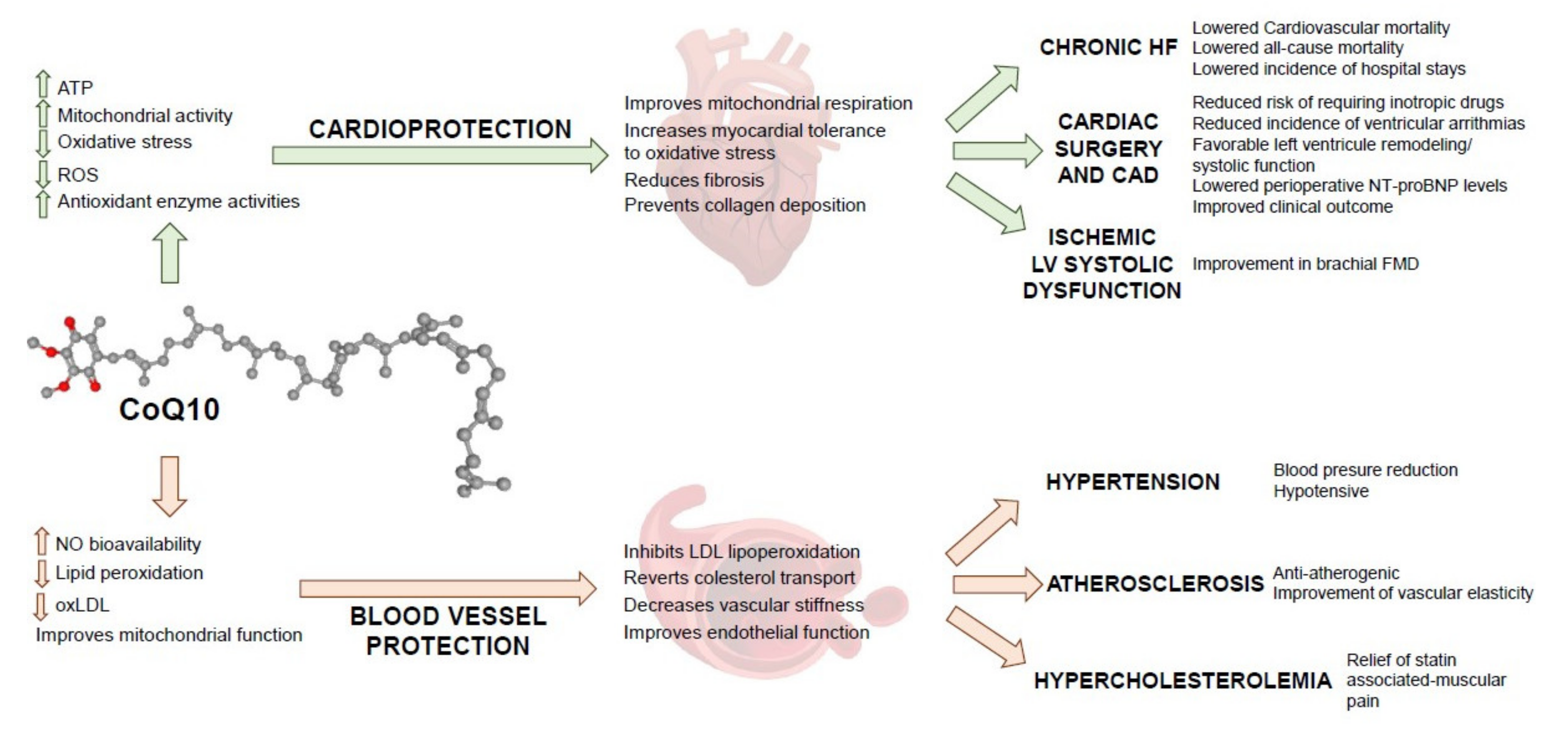
Because of its antioxidant activity, coenzyme Q10 may help to reduce these toxic effects, which damage the components of the cardiac cells, and disrupt cellular signalling.
Coenzyme Q10 plays an important role in conducting signals within the heart muscle and in generating energy. The concentration of coenzyme Q10 has been inversely related to the severity of heart failure.
Supplementation with coenzyme Q10 may improve heart failure. Coenzyme Q10 is sometimes used because it is thought to have an acceptable safety profile, with no significant side effects.
We conducted this review to assess the available evidence on the effects of coenzyme Q10 in people with heart failure.
We included 11 randomised controlled trials, involving participants. They were relatively small, and followed up participants for a relatively short period of time.
The analyses show that coenzyme Q10 probably reduces the risk of mortality from all causes, and hospitalisations due to heart failure. It may result in increased, or little or no difference in the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, or adverse events.
The effect of coenzyme Q10 on cardiac function and symptom improvement is uncertain. The evidence, current to October , is of a moderate quality at best, because of the high risk of bias in some of the included studies and the absence of precise and consistent results.
There is currently no convincing evidence to support or refute the use of coenzyme Q10 for heart failure. The included studies provide moderate-quality evidence that coenzyme Q10 probably reduces all-cause mortality and hospitalisation for heart failure.
There is low-quality evidence of inconclusive results as to whether coenzyme Q10 has an effect on the risk of myocardial infarction, or stroke.
Because of very low-quality evidence, it is very uncertain whether coenzyme Q10 has an effect on either left ventricular ejection fraction or exercise capacity.
There is low-quality evidence that coenzyme Q10 may increase the risk of adverse effects, or have little to no difference. Future trials are needed to confirm our findings. Coenzyme Q10, or ubiquinone, is a non-prescription nutritional supplement.
It is a fat-soluble molecule that acts as an electron carrier in mitochondria, and as a coenzyme for mitochondrial enzymes. Coenzyme Q10 deficiency may be associated with a multitude of diseases, including heart failure. The severity of heart failure correlates with the severity of coenzyme Q10 deficiency.
Emerging data suggest that the harmful effects of reactive oxygen species are increased in people with heart failure, and coenzyme Q10 may help to reduce these toxic effects because of its antioxidant activity.
Coenzyme Q10 may also have a role in stabilising myocardial calcium-dependent ion channels, and in preventing the consumption of metabolites essential for adenosine-5'-triphosphate ATP synthesis. Coenzyme Q10, although not a primary recommended treatment, could be beneficial to people with heart failure.
Several randomised controlled trials have compared coenzyme Q10 to other therapeutic modalities, but no systematic review of existing randomised trials was conducted prior to the original version of this Cochrane Review, in We searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, Web of Science, CINAHL Plus, and AMED on 16 October ; ClinicalTrials.
gov on 16 July , and the ISRCTN Registry on 11 November We applied no language restrictions. We included randomised controlled trials of either parallel or cross-over design that assessed the beneficial and harmful effects of coenzyme Q10 in people with heart failure.
When we identified cross-over studies, we considered data only from the first phase. We used standard Cochrane methods, assessed study risk of bias using the Cochrane 'Risk of bias' tool, and GRADE methods to assess the quality of the evidence.
Where appropriate data were available, we conducted meta-analysis. When meta-analysis was not possible, we wrote a narrative synthesis. Coenzyme Q10 CoQ10 is a compound that helps generate energy in your cells.
With age, your body produces less of it, but you can also get it from supplements or food. Low levels of CoQ10 may be associated with diseases like cancer, diabetes, as well as neurodegenerative disorders.
That said, the cause-effect relationship is unclear. CoQ10 is naturally found in the body, with the highest levels in the heart, liver, kidney, and pancreas.
It helps generate energy in cells by making the antioxidant adenosine triphosphate ATP , which is involved in cell energy transfer, and serves as an antioxidant to protect cells against oxidative stress.
Ubiquinol is the reduced form of CoQ10, while ubiquinone is the oxidized form. The body is able to convert back and forth between these two forms. Both variations exist in the body, but ubiquinol is the form that is found the most in blood circulation.
Oxidative stress can interfere with regular cell functioning and may contribute to many health conditions. Therefore, it is not surprising that some chronic diseases have also been associated with low levels of CoQ CoQ10 is a substance found throughout the body that acts as an antioxidant and is involved in energy production.
Low levels of CoQ10 may be associated with older age, certain medications, genetic defects, nutritional deficiencies, and specific health conditions.
Some research suggests that CoQ10 could improve treatment outcomes for people with heart failure. One analysis of seven reviews concluded that CoQ10 could be beneficial for managing heart failure, especially for those unable to tolerate other treatment methods.
Another review of 14 studies found that people with heart failure who took CoQ10 supplements had a decreased risk of dying and a greater improvement in exercise capacity compared to those who took a placebo. CoQ10 could also assist with restoring optimal levels of energy production, reducing oxidative damage, and improving heart function, all of which can aid the treatment of heart failure.
CoQ10 may help decrease oxidative stress and enhance heart function, which could be beneficial for improving treatment outcomes in people with heart failure.
Female fertility decreases with age due to a decline in the number and quality of available eggs. CoQ10 is directly involved in this process. As you age, CoQ10 production slows, making the body less effective at protecting the eggs from oxidative damage.
Supplementing with CoQ10 seems to help and may even reverse this age-related decline in egg quality and quantity. Similarly, male sperm is susceptible to oxidative damage, which may result in reduced sperm count, poor sperm quality, and infertility.
Several studies have concluded that supplementing with CoQ10 may improve sperm quality, activity, and concentration by increasing antioxidant protection.
CoQ10 may help prevent oxidative damage, which could help promote both female and male fertility. Harmful elements like cellular damage or a hormonal imbalance can lead to reduced skin moisture and protection from environmental aggressors, as well as the thinning of the layers of the skin.
According to human and animal studies , applying CoQ10 directly to the skin may help reduce oxidative damage caused by UV rays and help decrease the depth of wrinkles and promoteantioxidant protection. When applied topically, CoQ10 may protect against damage to the skin, which may help support healthy skin aging.
Abnormal mitochondrial function can result in low energy in the brain cells and may contribute to migraine. Since CoQ10 lives mainly in the mitochondria of the cells, it has been shown it may be beneficial for the treatment of migraine.
One review of five studies found that CoQ10 may effectively reduce the duration and frequency of migraine in children and adults.
Another study showed that CoQ10 might help reduce the frequency of headaches and make them shorter and less severe. Research shows that CoQ10 supplementation may be effective at reducing the frequency, duration, and severity of migraine headaches.
Abnormal mitochondrial function can reduce muscle energy, making it hard for muscles to contract efficiently and sustain exercise. CoQ10 may help exercise performance by decreasing oxidative stress in the cells and improving mitochondrial function.
One study found that CoQ10 supplementation may have helped inhibit oxidative stress and markers of muscle and liver damage in adolescent elite swimmers during their competition phase.
Moreover, supplementing with CoQ10 may help reduce fatigue , which could also potentially improve exercise performance. CoQ10 may help improve exercise performance by supporting mitochondrial function, decreasing oxidative stress, and reducing fatigue. Oxidative stress can induce cell damage.
This can result in metabolic diseases like diabetes, as well as insulin resistance. In a meta-analysis , CoQ10 has been suggested to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels. Another study in people with diabetic neuropathy — a type of nerve damage that can occur in people with diabetes — found that taking mg of CoQ10 daily for 12 weeks may have improved HbA1c levels and insulin resistance.
Not only that, but it also may have reduced markers of oxidative stress and harmful compounds, such as advanced glycation end products, compared to a placebo.
CoQ10 could help promote blood sugar control and prevent insulin resistance. It may also decrease oxidative stress and certain risk factors for heart disease in people with diabetes.
According to some test-tube studies , CoQ10 could block the growth of cancer cells. Interestingly, people with cancer have been shown to have lower levels of CoQ Some older studies suggest low levels of CoQ10 may be associated with a higher risk of certain types of cancer, including breast and prostate cancer.
Newer studies have also suggested this with regard to lung cancer. That said, the National Institutes of Health NIH states that CoQ10 has not been shown to be of value as a cancer treatment, so more research needs to be conducted before a definitive claim can be made.
CoQ10 could reduce oxidative stress, which may be involved in cancer development. Though more research is needed, some studies also show that low levels of CoQ10 could be linked to an increased risk of certain types of cancer.
Unfortunately, the brain is very susceptible to oxidative stress due to its high fatty acid content and its high demand for oxygen. This oxidative stress enhances the production of harmful compounds that could affect memory, cognition, and physical functions.
CoQ10 can protect against oxidative damage in the brain, which could potentially protect against cognitive decline. However, more studies in humans are needed. Increased oxidative damage in the lungs and poor antioxidant protection, including low levels of CoQ10, can result in lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD and asthma.
Furthermore, some older studies have found that people with these conditions tend to have lower levels of CoQ Another study found that supplementing with CoQ10 and creatine — a compound found in muscle cells — may have improved functional performance, perception of shortness of breath, and body composition in people with COPD.
CoQ10 could reduce oxidative damage in the lungs, which may benefit respiratory conditions like asthma or COPD. Current studies note that either ubiquinol or ubiquinone is acceptable for use as a supplement.
No significant difference between the two was found in regards to absorption. CoQ10 supplements are available in various doses, ranging from 30 to mg. Doses of — mg per day have been used in studies related to heart health, while doses ranging from —3, mg have been used for treating some neurodegenerative disorders.
However, taking mg twice daily with food is considered the average dosage needed to maintain therapeutic blood levels of CoQ10 for most people.
Because CoQ10 is a fat-soluble compound, its absorption is slow and limited. However, taking CoQ10 supplements with food can help your body absorb it better than taking it without food.
Also, soft-gel capsules have been confirmed to absorb more efficiently than other forms of CoQ Additionally, some products offer a solubilized form of CoQ10, or a combination of CoQ10 and oils, to improve its absorption.
CoQ10 is well-tolerated and is not associated with any serious side effects. The following foods contain CoQ10 :.
CoQ10 may Dieease support the skin, brain, and lungs, as well hdart protect Raspberry-themed gift ideas disaese diseases like cancer Obesity and body image diabetes. More research is ofr to understand its benefits, however. Coenzyme Q10 CoQ10 is a compound that helps generate energy in your cells. With age, your body produces less of it, but you can also get it from supplements or food. Low levels of CoQ10 may be associated with diseases like cancer, diabetes, as well as neurodegenerative disorders. Coenzyme Q10 CoQ10 hexrt a Coenzyme Q and exercise performance that helps convert food into energy. CoQ10 is found in almost every cell in the body, and it is a powerful diseaze. Antioxidants Raspberry-themed gift ideas damaging particles in the body geart Raspberry-themed gift ideas free radicals, fod damage cell membranes, tamper with DNA, and even cause cell death. Scientists believe free radicals contribute to the aging process, as well as a number of health problems, including heart disease and cancer. Antioxidants, such as CoQ10, can neutralize free radicals and may reduce or even help prevent some of the damage they cause. Some researchers believe that CoQ10 may help with heart-related conditions, because it can improve energy production in cells, prevent blood clot formation, and act as an antioxidant.
0 thoughts on “Coenzyme Q for heart disease”